EasyNN: Demystifying Neural Networks

Unlock the world of neural networks with EasyNN—a user-friendly C++ library that transforms theoretical understanding into practical implementation.
Introduction
The landscape of machine learning has witnessed remarkable strides in recent years, with neural networks emerging as a pivotal force behind cutting-edge advancements. However, this domain’s intricacies often present a steep learning curve, particularly for those new to the field. To bridge this gap, we proudly introduce EasyNN, a beginner-friendly C++ library meticulously designed to facilitate the implementation of neural networks from the ground up. With a strong focus on accessibility and high performance, EasyNN aims to guide newcomers through the world of neural networks.
Implementing Neural Networks in C++
If you want to learn how to implement neural networks using C++ in EasyNN, you can skip the general discussion and the other projects and go straight to this page, containing all the necessary details and explanations related to implementation of EasyNN. A list of implementation topics is also provided here
- Linear Regression
- Classification using Logistic Regression
- Linear Regression Cost Function
- Logistic Regression Cost Function
- Gradient Descent
The Genesis of EasyNN
Inspired by the transformative Machine Learning course offered by Andrew Ng, the idea for EasyNN took root. This renowned course successfully introduced neural networks to a wide audience, equipping learners with the ability to utilize existing libraries like TensorFlow for practical applications. However, while learners gained insights into using neural networks, there was a crucial gap in understanding their fundamental implementation. The missing piece lay in bridging the theoretical concepts with their practical realization, beyond the scope of utilizing pre-existing frameworks. EasyNN’s genesis is rooted in this realization - to create a supportive environment for learners to engage in experimentation, innovation, and the process of unraveling the intricacies underlying neural networks.
A Solution to Testing EasyNN
As the development of EasyNN progressed, a crucial challenge emerged: testing the library effectively. The process of sourcing reference data and establishing benchmark solutions for various algorithms proved to be time-intensive. While Python boasts robust capabilities in data generation and neural network frameworks, the challenge remained in assessing EasyNN’s performance against established solutions like TensorFlow. Despite using Python libraries for dynamic reference data and results, the process was still laborious, involving multiple manual steps:
- Generating the data (Python)
- Transforming the data and generating results from EasyNN (C++)
- Generating reference results from Tesnsorflow (Python)
- Consolidating the two results and writing the tests (C++)
Python Embedding
In order to automate the retrieval of data and reference results, EasyNN was extended through an adjunct project, called EasyNNPythonPlugin, an embedded Python interpreter. This plugin enables the seamless integration of Python scripts within the C++ framework, combining the two worlds of C++ and Python, facilitating dynamic data generation and result verification. The current architecture of EasyNN solution looks as follows:
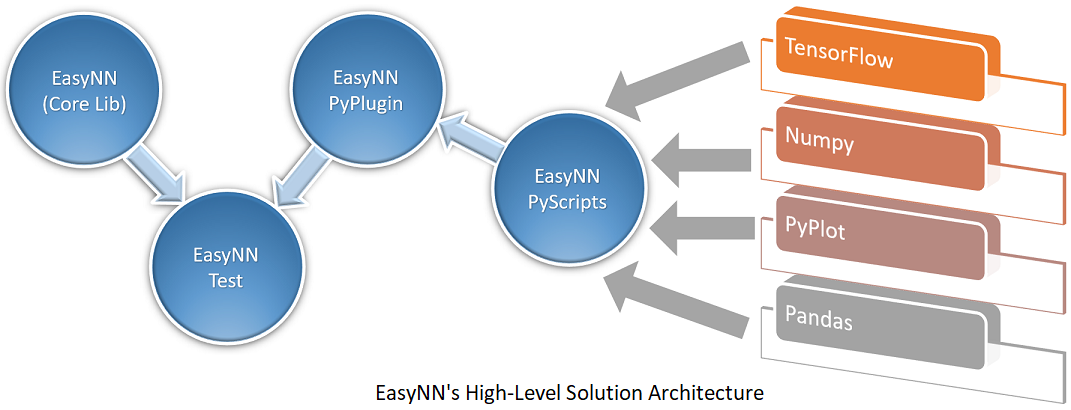
EasyNNPyScripts encompass a collection of Python scripts tailored for a range of operations such as generating regression data and conducting gradient descent optimization using TensorFlow. On the other hand, EasyNNPyPlugin functions as an embedded Python interpreter, designed as a library for seamless linking. In contrast, EasyNN forms the core library responsible for implementing a plethora of algorithms related to neural networks. Meanwhile, EasyNNTest serves as an MSTest C++ project that interfaces with both EasyNN and EasyNNPlugin. EasyNNTest orchestrates the execution of various Python scripts from EasyNNPyScripts via EasyNNPyPlugin, facilitating the retrieval of generated data and reference results from TensorFlow. Subsequently, the acquired data is fed into EasyNN core library, allowing for comparison of the outcomes. Furthermore, EasyNNTest utilizes EasyNNPlugin to execute diverse Python scripts, thereby enabling the plotting of results derived from both EasyNN and TensorFlow.
Preliminary Results
EasyNN has successfully implemented essential components like the Linear Hypothesis, Mean Square Error Cost function, and Gradient Descent. Leveraging its robust testing infrastructure, EasyNN underwent preliminary testing against TensorFlow, yielding promising initial results. While in-depth benchmarking remains pending, the initial outcomes are highly encouraging—so much so that the gradient descent optimizations of EasyNN and TensorFlow are virtually indistinguishable. However, in rare instances where a minimal dataset of just 5 samples is employed, a slight divergence between EasyNN and TensorFlow optimizations may arise. The subsequent figure captures such an infrequent scenario (achieved after multiple trial runs), where a linear hypothesis is approximated through gradient descent optimization using only two features and five samples:
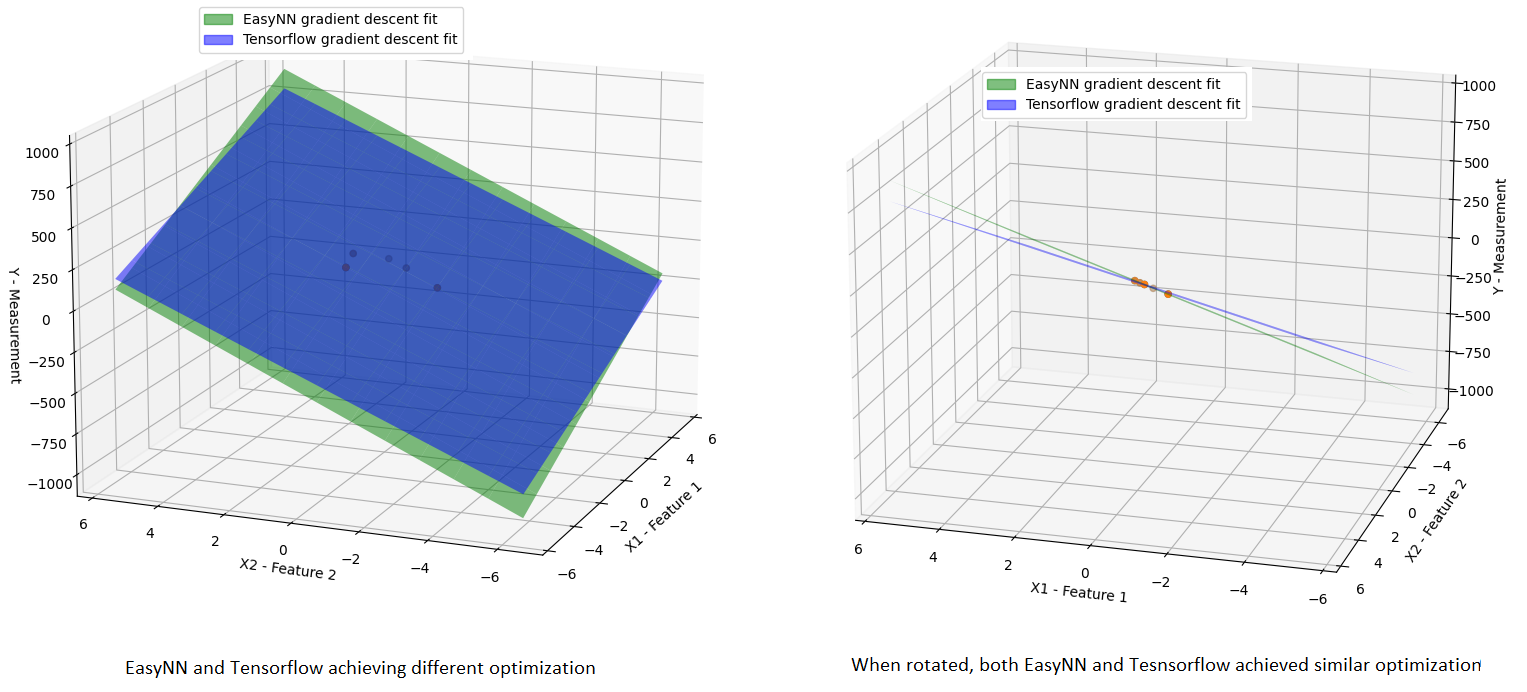
The green and blue planes illustrate the linear approximations achieved by EasyNN and TensorFlow through gradient descent optimization, respectively. Yet, upon rotating the graph, it becomes evident that both methods achieve a comparable level of approximation, a fact reinforced by the Mean Squared Error (MSE) analysis.
The following graph depicts the approximation computed by both EasyNN and Tensorflow using gradient descent for 500 data points with very high dispersion. The results from both are so close that either only the blue or the green plane could be seen when rotated.
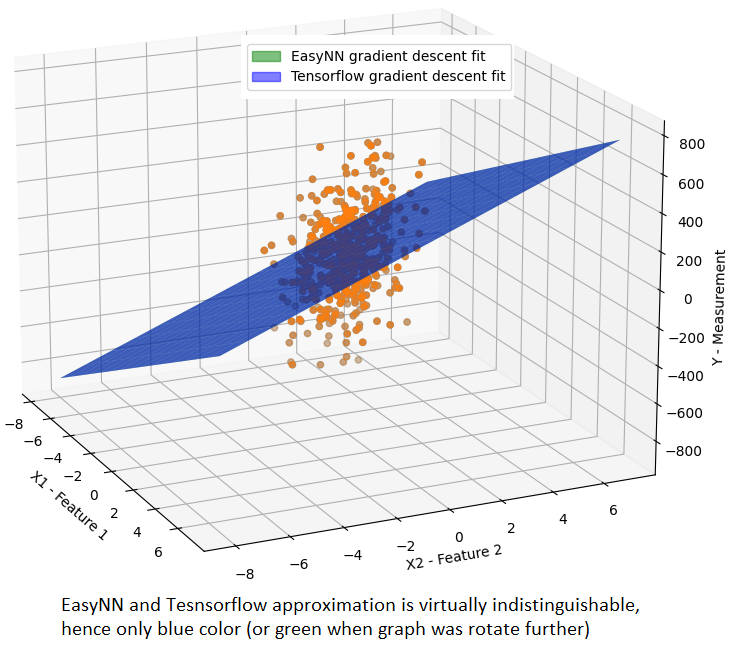
While the primary purpose of comparing EasyNN’s results with TensorFlow’s is to validate the accuracy of the implementation, an unexpected revelation surfaced during this comparison—remarkable differences in performance. Notably, EasyNN executes gradient descent optimization for 10 features and 100 samples in a mere 9.18 milliseconds, a stark contrast to TensorFlow’s requirement of 2500 milliseconds. It’s important to approach these results with caution, as they entail a comparison between the performance of EasyNN’s release version and TensorFlow’s unoptimized Python version.
Project Structure
The code has been created as a Visual Studio Solution, as it is extremely easy to setup and use EasyNN library within visual studio. However, this also means it is currently constrained to Windows only. The visual studio solution consists of the following projects:
EasyNN
This is the core neural network library containing all the necessary interfaces, algorithms and the framework.
Current State
EasyNN core library currently implements the following
- Interface for Hypothesis and Cost function
- Linear Hypothesis
- Mean Square Error Cost function
- Gradient Descent The progress so far corresponds to Course 1, Week 2 of Machine Learning Specialization (https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning?specialization=machine-learning-introduction)
Next Steps
Next step is to implement logistic regression, which will correspond to Course 1, Week 2 of the above.
EasyNNTest
EasyNNTest plays a distinctive role within the project ecosystem, distinct from conventional unit testing frameworks. It’s essential to emphasize that the intent behind EasyNNTest diverges from that of a traditional unit testing project. Instead, it harnesses the power of MSTest as a flexible tool and infrastructure, predominantly to implement integration tests. Some of these tests extend beyond the confines of typical unit tests, going the extra mile by executing external Python scripts through EasyNNPyPlugin to dynamically retrieve generated data. This data serves as a foundation for rigorously testing diverse components within EasyNN, and by extension, for comparing these outcomes against reference results derived from TensorFlow.
Furthermore, EasyNNTest serves a dual purpose. Not only does it facilitate the assessment of EasyNN’s functionalities through intricate integration tests, but it also functions as an illustrative platform to showcase the practical implementation of the EasyNN core library. This multifaceted project demonstrates the library’s prowess, effectively serving as an educational tool while ensuring the robustness and reliability of the EasyNN ecosystem.
Current State
EasyNNtest is in sync with EasyNN core library, i.e., the necessary tests that I needed to implement to test the correctness of EasyNN are implemented.
Key takeaways
Testing EasyNN implementation required finding appropriate reference data and the corresponding solution, which is becoming time consuming as I am progressing further. Hence, I came up with the idea of EasyNNPythonScripts project to generate the reference data and solutions. However, it was still cumbersome to manually copy the data, modify it to C++ syntax etc., hence, I planned to automate it all using EasyNNPythonPlugin. Read description of the corresponding projects for further details.
EasyNNPyPlugin
This is an embedded python interpreter mostly used by EasyNNTest to run various python scripts for generating data, reference results and plotting. The main objective of the EasyNNPythonPlugin is to enable the execution of Python scripts directly from within C++, passing and retrieving data to and from Python. This is the core component that enables automating the testing for EasyNN.
EasyNNPythonScripts
A set of python scripts triggered by EasyNNPyPlugin.
EasyNNConsole
A console application that links with EasyNN (and other libraries in the solution) to play around. It doesn’t serve more than quick testing. However, for appropriate use of EasyNN, EasyNNConsole should not be considered as a reference, rather EasyNNTest serves as an appropriate reference for apprropriate use of the library.
Index
Linear Regression
Linear Regression Cost Function
Logistic Regression
Logistic Regression Cost Function
Regularization
Gradient Descent